DIETARY GUIDELINES #EAT HEALTHY

Food Pyramid
India is witnessing a rapidly changing food landscape influenced by lifestyle changes, food habits, and scientific findings.New estimates reveal that 56.4% of the country’s disease burden is due to unhealthy diets.
Additionally, food systems contribute to one-third of greenhouse gas emissions.To address these challenges, adhering to updated dietary guidelines is essential.
These guidelines promote sustainable eating practices and the consumption of foods produced in an economically, socially, and environmentally responsible manner, aiming to improve public health and reduce environmental impact.
CURRENT FOOD HABITS AND CONCERN

The transition in India’s food habits is troubling. The population is increasingly consuming packaged and processed foods, as well as meals cooked outside the home.
This shift has led to a reduction in the variety of food choices and a loss of knowledge about local biodiversity’s potential as food.
The consumption of intensively grown produce and processed foods is prevalent, raising health concerns.
NEW DIETARY GUIDELINES

To combat these issues, the Indian Council of Medical Research (ICMR) and the National Institute of Nutrition (NIN) have issued 17 dietary guidelines. These guidelines aim to meet essential nutrient requirements and prevent non-communicable diseases such as obesity and diabetes. They emphasise a balanced diet, food groups, and variety, making it easier for people to understand and apply them.
The guidelines provide specific recommendations for different physiological needs, including children, nursing mothers, and the elderly, and offer options for both vegetarian and non-vegetarian diets.
KEY RECOMMENDATIONS
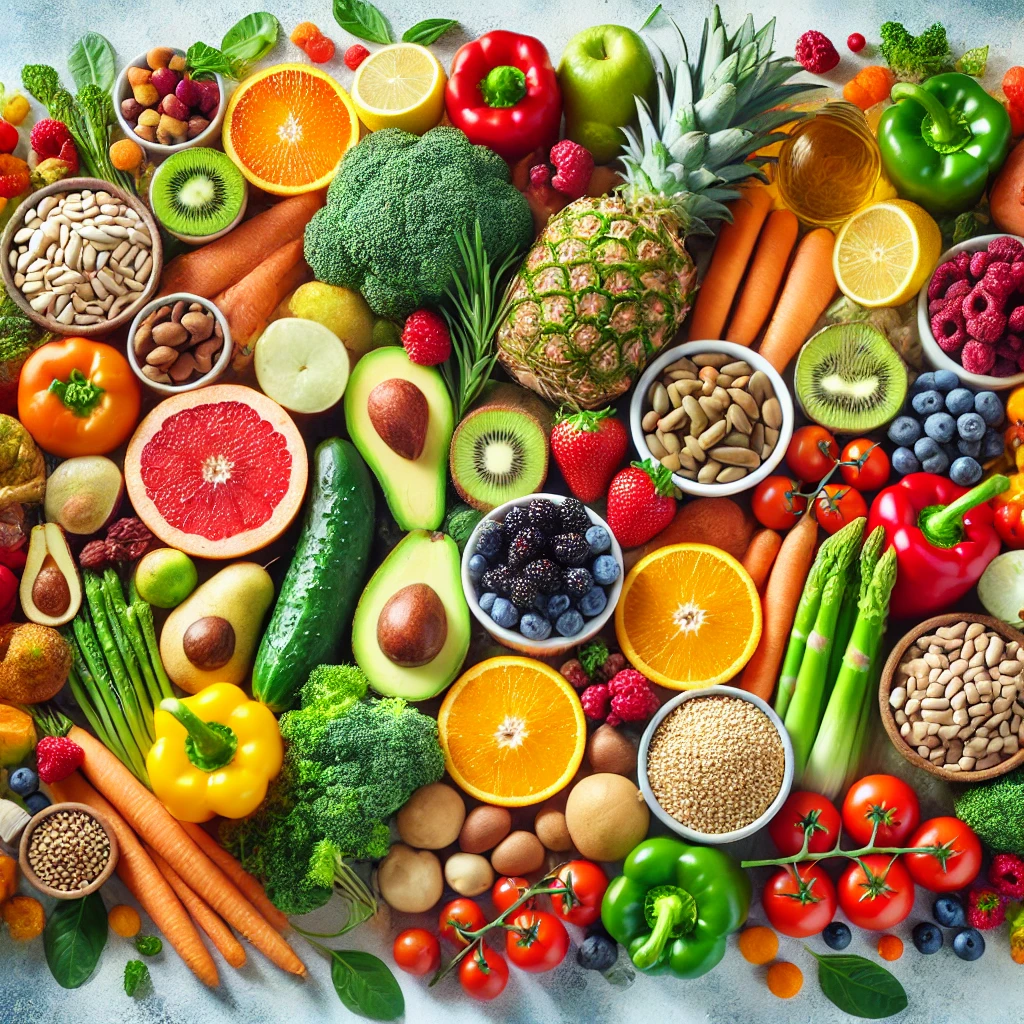

The ICMR diet booklet advises deriving macronutrients and micronutrients from at least eight food groups daily. It recommends that vegetables, fruits, roots, and tubers compose about half of the daily food intake, with cereals, millets, pulses, eggs, nuts, oilseeds, and milk making up the remaining portion.
Vegetarians are encouraged to include foods like flax seeds and chia seeds to ensure adequate intake of B12 and N3 polyunsaturated fatty acids.
SUGAR AND PROTEIN INTAKE

ICMR suggests reducing calories from sugar to less than 5% of daily caloric intake, limiting sugar consumption to around 30 grams a day, and avoiding sugar for children under two years old. Long-term use of sugar substitutes like aspartame and saccharine can lead to obesity, diabetes, hypertension, and other non-communicable diseases.
The guidelines also caution against high protein intake from supplement powders due to risks like kidney damage, dehydration, and nutrient imbalances.
EMBRACING LOCAL BIODIVERSITY

The guidelines advocate for incorporating local biodiversity into diets by consuming local greens, fruits, and legumes, which are rich in micronutrients. This approach can help address concerns about nutrient deficiencies and promote sustainable eating practices.
LABELLING AND CONSUMER AWARENESS
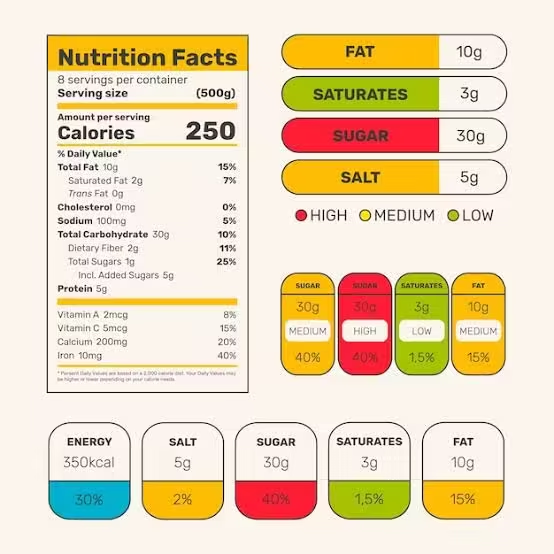
The guidelines highlight the importance of understanding nutrition fact labelling, which is often complex and primarily in English. Clear and accessible labelling can help consumers make informed choices.
The guidelines align with the goals set in the National Nutrition Policy and National Policies for Agriculture and Health.
CONCLUSION
In a nation rich with culture and diversity, one of India’s greatest challenges is the battle for good health.
These comprehensive guidelines target vulnerable groups, offering tailored recommendations to promote optimal nutrition and combat the rise of non-communicable diseases.
By adhering to these guidelines, individuals can significantly reduce their risk of developing diseases such as diabetes, hypertension, and cardiovascular diseases.
The journey toward better health is illuminated by these guidelines, empowering individuals and communities to make informed choices and embrace a future of wellness and vitality.
However, implementing these guidelines and ensuring they reach the masses remains a critical step to transform these recommendations from paper to practice.
FOR MORE FOLLOW






Pingback: KEY PARENTAL ROLE IN CHILD DEVELOPMENT AND SUCCESS-THE KNOWLEDGE LOOM
Pingback: KITCHEN GARDEN: A PATH TO HEALTHY FOOD - THE KNOWLEDGE LOOM