Understanding the Thyroid
What is the Thyroid?
The thyroid is a gland located in the neck that produces two major hormones: T4 (thyroxine) and T3 (triiodothyronine). These hormones regulate the body’s metabolism, energy production, and many other vital functions.
Can “Thyroid” Be Used to Describe a Disease?
No, the term “thyroid” refers to the gland itself. There are several diseases related to the thyroid, including hypothyroidism, hyperthyroidism, thyroiditis, goiter, and thyroid cancer. However, people often mistakenly refer to hypothyroidism as “thyroid.”
Prevalence of Hypothyroidism
Hypothyroidism affects about 11% of people. In this condition, relatively less T4 and T3 hormones are produced, and TSH levels increase.
Symptoms of Hypothyroidism

Childhood
• Mental and physical development may stop.
Young Age
• Lethargy
• Weight gain
• Menstrual problems in women
• Frequent miscarriages
• Infertility
Old Age
• Lethargy
• Weakness
• Swelling
• Weight gain
• Heart weakness
• Increased cholesterol
• Snoring
Both men and women can suffer from hypothyroidism.
What is Hyperthyroidism?
In hyperthyroidism, T4 and T3 hormones are produced in large amounts, and TSH decreases. About 1.6% of people are affected by this condition.
Symptoms of Hyperthyroidism
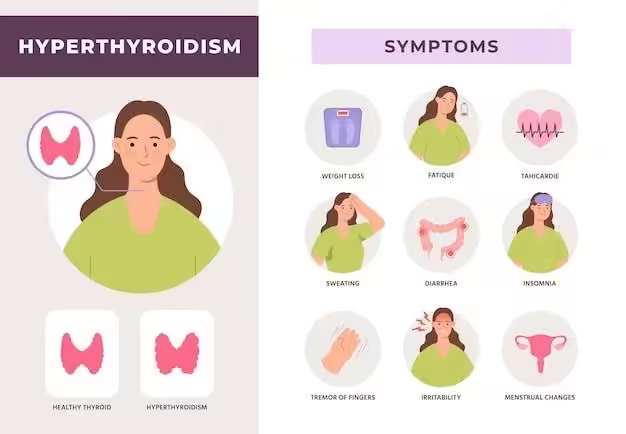
• Weight loss
• Fever
• Tremors in hands and legs
• Increased heartbeat
• Proptosis (bulging of the eyes)
• Some people may develop certain heart diseases or osteoporosis (weakening of the bones).
Is Thyroid Disease Lifelong?
Thyroid disease often lasts a long time. About 35% of hyperthyroidism patients recover within one or two years, but 65% suffer for a long time. Hypothyroidism is typically a lifelong condition.
Does Thyroid Treatment Make a Difference?
Yes, proper treatment improves the quality of life and can prevent heart diseases. It also helps in treating infertility in women and ensures the physical and mental development of children.
Managing Eye Symptoms in Hyperthyroidism
Proper control of the disease and the use of corticosteroid medications can be beneficial for patients experiencing proptosis.
Treatments for Thyroid Disease
Treatment options include medications, surgery, and nuclear medicine, depending on the type and condition of the disease.
Importance of Thyroid Control During Pregnancy
Proper thyroid control ensures the mental development of the child and helps prevent miscarriages.
Medication Safety During Pregnancy
Hypothyroid medications are safe during pregnancy. However, hyperthyroid medications should be avoided in the first three months.
Gender Differences in Thyroid Disease
Women are more frequently affected by thyroid diseases than men, with a ratio of 6:1.
Key Points to Remember
• The thyroid gland plays a crucial role in regulating the body’s metabolism and overall health.
• Thyroid disease, including hypothyroidism and hyperthyroidism, require proper diagnosis and treatment to manage symptoms and prevent complications.
• Regular monitoring and appropriate treatment can significantly improve the quality of life for individuals with thyroid conditions.
• Awareness and education about thyroid health are essential for early detection and effective management of thyroid-related diseases.
Understanding the functions of the thyroid gland and recognising the symptoms of thyroid diseases can lead to better health outcomes.
Proper treatment and management of thyroid conditions are vital for maintaining overall health and well-being.
If you suspect any thyroid-related issues, it is essential to consult a healthcare professional for appropriate diagnosis and treatment.






Pingback: PHNOM PENH: A WONDER FOR TOURISTS-THE KNOWLEDGE LOOM